Mucosal melanoma
Mucosal melanoma forms in the mucous membrane that lines the nose, mouth, esophagus, anus, urinary tract, and vagina. Mucosal melanomas are particularly difficult to detect because they can be confused with other, much more common diseases.
Melanoma in the eye
Mucosal melanoma forms in the mucous membrane that lines the nose, mouth, esophagus, anus, urinary tract, and vagina. Mucosal melanomas are particularly difficult to detect because they can be confused with other, much more common diseases.
malignant melanoma
This skin cancer can develop from a mole (melanocytic nevus) present from birth (congenital) or acquired (developed after birth). It can also develop from an area of skin without a mole as a growing spot that later transforms into a tumor. The incidence of melanoma around the world has grown alarmingly. It is estimated that up to 1 in every 50-70 Spaniards will develop melanoma throughout their lives in 2010. Melanoma is a cancer that usually does not usually hurt or have warning symptoms until it has developed and spread to the lymph nodes or other organs through the blood circulation. Usually the patient does not think that it can be so dangerous or is not able to detect its appearance in the early stages. When a melanoma has become a palpable skin tumor or has a bleeding episode, it may be too late. For this reason, early diagnosis and correct removal when it is located on the skin is essential.
Melanoma
Melanoma is a type of skin cancer, the most serious. The first sign of melanoma is a change in color, size, and shape of a mole.
Melanomas usually have a black or bluish area. It may appear as a new, abnormally black or unpleasant-looking mole.
It is important to prevent moles in time and monitor them thinking about the “ABCDE” Asymmetry, the contours are different Irregular edges Different colors Diameter, the moles increase in size.
Evolution: any change in the mole Surgery is the first treatment for melanoma.
Nail melanoma
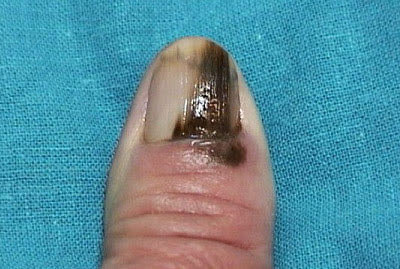
Acral lentiginous melanoma is a rare form of melanoma that can occur under a toenail or fingernail. It can also be found on the palms of the hands or the soles of the feet. It is more common in people of Asian descent, black people, and others with dark skin pigment.
Invasive melanoma
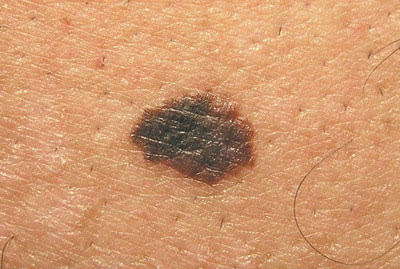
Invasive melanoma is a cancer that can spread to other parts of the body. Melanoma is divided into stages based on the thickness of the primary tumor and other characteristics. The thickness of a tumor is the most important risk factor. The thicker the tumor, the more likely it is to spread.
Melanoma in situ
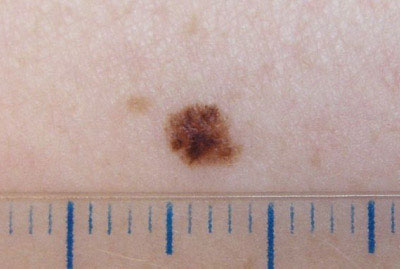
Stage 0 melanomas (melanoma in situ) have not grown outside the top layer of skin (the epidermis). It is usually treated with surgery (wide excision) to remove the melanoma and a small margin of normal skin around it. The extracted sample is then sent to a laboratory to be observed under a microscope. If cancer cells are seen at the edges of the sample, a second, wider excision may be done in the area.
squamous cell carcinoma
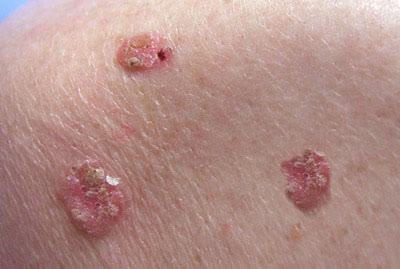
One of the types of skin cancer highly related to accumulated sun damage on the skin. In cases of highly evolved and/or incorrectly treated tumors, they can become aggressive, although nowadays they can usually be prevented and treated efficiently when detected in the initial stages. They usually present as red, scaly, raised, crusty, often painful areas in areas with marked chronic sun damage and photoaging. In some patients it can invade locally or even the nodes.
Basal cell carcinoma
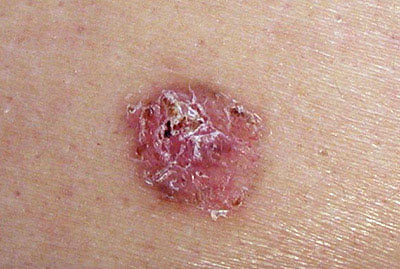
The most common and low-risk type of skin cancer as long as it is treated correctly. It has no ability to spread beyond the skin unless it is allowed to evolve for years without treatment. It usually presents as a shiny, reddish or somewhat darkly pigmented area, usually presents small erosions or superficial wounds, and does not usually cause any discomfort but does not resolve without adequate treatment. Currently, dermatologists who are experts in the field have the ability to detect it when they are millimetric and on some occasions it can progress or invade very superficial areas, so that its treatment can be performed even with barely invasive techniques and leaving minimal scarring.

